Overview
This report presents the findings of a survey undertaken in east and central Delhi to gauge how residential consumers perceive rooftop solar technology, their levels of awareness, and their willingness to accept new business models. The report also highlights the drivers and barriers to the adoption of rooftop solar in India. The survey, undertaken in collaboration with BSES Yamuna Private Limited (BYPL) – a Delhi-based power distribution company – follows a study that recommended innovative distribution company-led business models to accelerate the deployment of rooftop solar in the residential sector.
As of December 2018, the installed capacity of rooftop solar in India stands at 3.4 GW against a target of 40 GW to be achieved by 2022. The residential sector has contributed only 15 per cent so far despite its high technical potential. Lack of consumer awareness, lack of access to suitable roof spaces, high upfront costs, lack of trust in solar companies, and subsidised electricity tariffs for residential consumers are some of the reasons behind the slow uptake of rooftop solar in the country.
Willingness to pay for a 1kW rooftop solar system
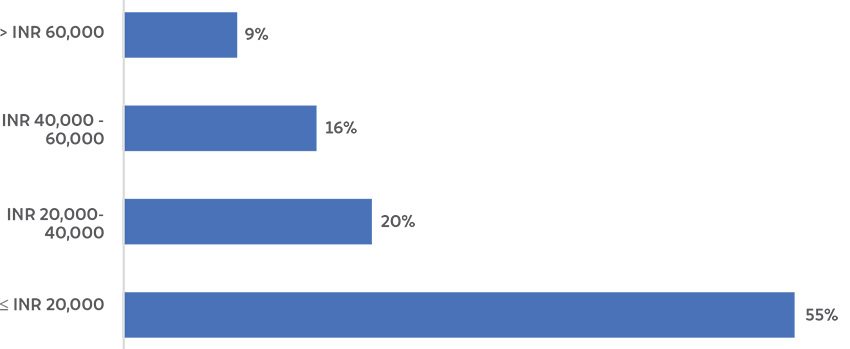
Source: Authors’ analysis
Key Findings
The study presents insights from data collected from 418 households in the BYPL licence area.
- Lack of awareness: While around 78 per cent of the consumers surveyed were aware that rooftop solar systems were being installed in the city, only 41 per cent knew at least one specific regarding the technology, costs, maintenance requirements, performance, and system life.
- Sources of information for residential consumers: Word of mouth emerged as the most common source of information for residential consumers, followed by solar vendors, television, and the distribution company.
- Low willingness to pay: Only 25 per cent of consumers expressed a willingness to pay the current rates (after capital subsidy) for rooftop solar. This might be due to a poor understanding of the economic benefits of installing a rooftop system. Only 26 per cent of consumers were aware of the decreasing trend in system costs.
- Acceptance of new business models: Given the high upfront cost of rooftop solar systems, financing options are also an important consideration in decision-making. A significant share of the surveyed consumers sought cheaper interest rates and expressed an interest in new business mechanisms, such as shared systems, on-bill financing, third-party ownership, and solar subscription models.
- Drivers and barriers: Environmental consciousness and the potential reduction in electricity expenditure – as stated by 78 per cent of respondents - are the key drivers for installing rooftop solar. The top two barriers were lack of awareness and lack of trusted solar companies.
Key Recommendations for Distribution Companies
- Create more awareness among residential consumers so that households can make informed investment decisions while considering rooftop solar as a viable option.
- Given that word of mouth and social influence play an important role in increasing awareness among consumers, use targeted campaigns and neighbourhood programmes to demonstrate and promote rooftop solar technology.
- Develop innovative financing mechanisms to make rooftop solar affordable for more consumers.
- Design and implement suitable market interventions in various consumer categories to increase adoption among residential consumers.

